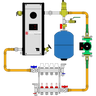
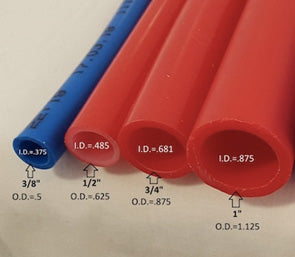
The effectiveness of hydronic radiant floor heating systems, known for their simplicity and efficiency, depends on several factors. One critical factor is the diameter of the tubes through which hot water circulates. This article will explore various PEX tube sizes, how they are determined, and their optimal applications.
What Determines PEX Tube Sizing?
Selecting the right tube size is crucial for ensuring both comfort for occupants and efficient system performance. This is because the diameter of the tube directly influences the flow rate of hot water, which in turn affects the heat output. Tubes with larger diameters deliver a greater volume of hot water over a given period (flow rate), thereby generating more heat per square foot of the floor compared to tubes with smaller diameters.
Choosing the correct tube size is also essential to ensure adequate coverage of the room where the heating system will be installed. Smaller tubes, with lower flow rates, have shorter maximum run lengths. In contrast, larger-diameter tubes, which have higher capacities, can cover longer distances. Consequently, larger spaces may require wider tubes to achieve the necessary run length and ensure complete coverage of the entire floor area.
Here's a concise overview of how tube diameters correlate with maximum runs:
The size of PEX tubes directly impacts the maximum length they can effectively cover in a radiant floor heating system. Smaller diameter tubes, with their lower flow rates, are suitable for shorter maximum runs.
In contrast, larger diameter tubes, which allow for higher flow rates, can cover longer distances. Therefore, the choice of tube diameter is critical in determining how effectively the heating system can distribute heat across the floor area.
| Pipe Diameter | Maximum Recommended Run Length |
| 1/2" | Not be over 300' |
| 5/8" | Should not be over 400' |
| 3/4" | Should not be over 500' |
Other factors influencing heat output include water pressure, temperature variations, and tube spacing. Adjusting these variables can significantly impact how much radiant heat the heating system emits and its overall efficiency.
It's crucial to note that water temperature is largely determined by the type of heating system chosen for the building. For example, a heat pump typically produces lower flow temperatures compared to a boiler. Understanding the specific water temperature requirements is essential when selecting the appropriate tube diameter and spacing for the radiant floor heating system to ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
The optimal sizes of PEX pipes vary according to specific applications. In general:
Smaller pipe diameters and wider spacing are well-suited for well-insulated, smaller spaces where achieving desired temperatures requires less heat output.
Conversely, larger areas or spaces that are harder to heat may necessitate wider pipes that are installed closer together to meet heating demands effectively.
While these guidelines generally apply, exceptions exist, with heat output requirements being the primary factor determining pipe sizing.
A ½-inch diameter PEX pipe is well-suited for most residential applications:
In efficiently insulated homes with minimal heat loss, a spacing of 12 inches on center is ideal. This spacing typically provides around 30 BTUs per square foot of floor area, maintaining a comfortable room temperature.
Homes that are poorly insulated and experience greater heat loss through exterior walls require a higher heat output, approximately 50 BTUs per square foot. Achieving this output involves laying the tubes closer together, typically at 9 inches on center.
For bathrooms where a slightly higher temperature is desired compared to living or dining areas, ½-inch diameter tubes may be spaced at 6 inches on center to ensure adequate heat generation.
These spacing recommendations ensure that the radiant floor heating system effectively meets heating requirements based on the specific characteristics and heating demands of each area within a home.
- Recommended Circuit Length: 300 feet
- Recommended Tube Spacing (OC): 9-12 inches
- Suggested Flow Rate: 0.6 GPM
- Floor Output: 22-30 BTU per square foot per hour
The ⅝-inch diameter PEX tube is an optimal choice for heating smaller commercial buildings, industrial spaces or snowmelt applications:
This slightly larger diameter tube provides approximately 30% more water volume compared to the ½-inch variant, allowing for a higher flow rate and increased heat output.
With a spacing of 12 inches on center, ⅝-inch pipes can generate around 50 BTUs per square foot of floor area, making them suitable for maintaining comfortable temperatures in small-to-medium commercial spaces.
In poorly insulated areas such as shops or hangars, where higher heat output is needed, grouping ⅝-inch tubes closer together at 6 inches on center can significantly boost heat production to approximately 150 BTUs per square foot.
For commercial buildings located in warmer climates where less heating is required, spacing the ⅝-inch tubes further apart, such as at 15 or 16 inches on center, can still provide sufficient heat output while optimizing installation costs.
These adjustments in tube spacing demonstrate the flexibility of ⅝-inch PEX tubes in adapting to varying heating demands and efficiency needs across different types of commercial spaces
- Recommended Circuit Length: 400 feet
- Recommended Tube Spacing (OC): 12-16 inches
- Suggested Flow Rate: 0.9 GPM
- Floor Output: 10-24 BTU per square foot per hour
The ¾-inch diameter PEX tube is the preferred choice for large commercial and industrial buildings, as well as for snow melt applications:
This larger diameter tube facilitates a significantly higher flow rate compared to ½-inch tubes, doubling the amount of water volume circulated.
Even when spaced at a standard 12 inches on center, ¾-inch tubes can produce a substantial 150 BTUs per square foot of floor area. This high heat output makes them ideal for effectively heating expansive commercial and industrial spaces.
In addition to indoor applications, ¾-inch pipes are also suitable for outdoor use beneath driveways and walkways to melt snow and ice. The same spacing and heat output principles apply, ensuring efficient snow melting capabilities.
These characteristics highlight the versatility and efficiency of ¾-inch PEX tubes in meeting the substantial heating demands of large-scale commercial and industrial environments, as well as providing effective snow melt solutions for outdoor areas.
- Recommended Circuit Length: 500 feet
- Recommended Tube Spacing (OC): 12-16 inches
- Suggested Flow Rate: 1.2 GPM
- Floor Output: 17-26 BTU per square foot per hour
Some useful information that may help in choosing between the different pipe diameters
1/2-inch vs. 5/8-inch Tubing
- 5/8-inch tubing averages about 6.4% more heat output than 1/2-inch tubing.
- At lower water temperatures (80°F), the difference is slightly higher (7%), and at higher water temperatures (120°F), it's slightly lower (5.9%).
5/8-inch vs. 3/4-inch Tubing
- The difference in heat output between 5/8-inch and 3/4-inch tubing is assumed to be relatively small.
- On average across all water temperatures, 3/4-inch tubing provides about 2.4% more heat output than 5/8-inch tubing.
- At 120°F water temperature, the gain increases slightly to 5.4%, whereas at 80°F water temperature, it decreases to 0.9%.
| PEX Pipe Diameter | Max GPM | Max Btu/H @15°F Delta T |
Max Btu/H @ 20°F Delta T |
Max Btu/H @25°F Delta T |
Max Btu/H @ 30°F Delta T |
| 1/2" | 2.3 | 17250 | 23000 | 28750 | 34000 |
| 5/8" | 3.3 | 24750 | 33000 | 41250 | 49500 |
| 3/4" | 4.6 | 34500 | 46000 | 57500 | 69000 |
| 1" | 7.5 | 56250 | 75000 | 93750 | 112500 |
Establishing the correct tube size is crucial for ensuring an efficient radiant heat flooring system. Each standard tube diameter serves ideal applications based on their specific capabilities:
- ½-inch: Ideal for residential applications, providing sufficient heat output for well-insulated homes with minimal heat loss.
- ⅝-inch: Suitable for small commercial and industrial spaces, offering increased water volume and higher heat output compared to ½-inch tubes.
- ¾-inch: Best suited for large commercial and industrial buildings, as well as for snow melt applications. This diameter provides a substantial flow rate and high heat output per square foot of floor area.
Choosing the appropriate tube size ensures that the radiant heating system operates effectively, meeting the heating requirements of different types of buildings and environments.